Nipah Virus: The southern state of Kerala in India, known for its natural beauty and backwaters, is currently grappling with a new health crisis. After successfully combating the COVID-19 pandemic, Kerala now faces the ominous resurgence of the Nipah virus. Two suspected deaths related to the Nipah virus have sent shockwaves through the region, prompting the state government to issue a health alert. In this article, we will explore the recent developments surrounding the Nipah virus outbreak in Kerala, including its transmission, symptoms, and the government’s response.

The Nipah Virus: A Deadly Threat
The Nipah virus is not a new adversary for Kerala. The state had previously experienced outbreaks in 2018 and 2021, leading to fatalities. The virus, named after the Malaysian village where it was first identified in 1999, belongs to the Paramyxoviridae family. It is known for its high mortality rate, making it a significant public health concern.
Transmission of the Nipah Virus
The World Health Organization (WHO) defines the Nipah virus as zoonotic, which means it primarily spreads from animals to humans. Fruit bats, also known as flying foxes, are believed to be the natural reservoir of the virus. Human infections can occur through direct contact with infected bats or their bodily fluids, as well as by consuming fruits contaminated with bat saliva or urine.
Additionally, human-to-human transmission of the Nipah virus has been documented, particularly in healthcare settings. Close contact with an infected person’s respiratory secretions, blood, or other bodily fluids can lead to the transmission of the virus. This mode of transmission presents a substantial challenge in controlling outbreaks.
Symptoms and Impact
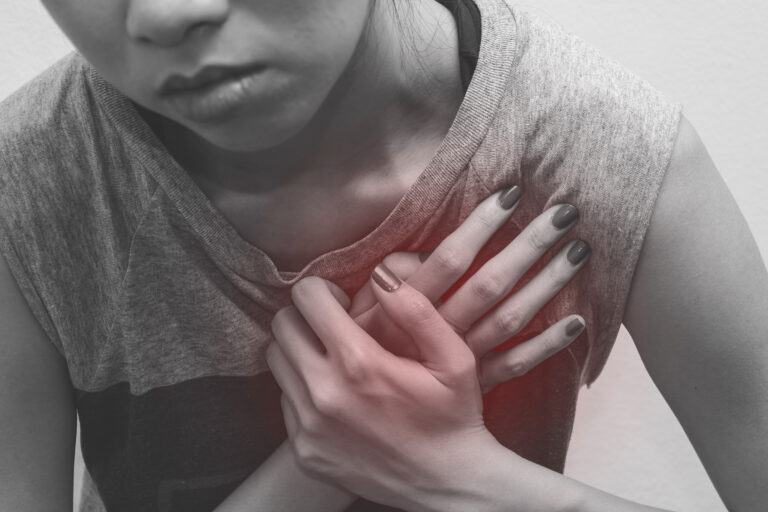
The Nipah virus infection can manifest in various ways, ranging from mild respiratory symptoms to severe encephalitis (inflammation of the brain). Common symptoms include fever, headache, dizziness, nausea, and vomiting. As the infection progresses, it can lead to seizures, altered consciousness, and ultimately, coma. The virus’s neurotropic nature, which affects the nervous system, makes it particularly dangerous.
Kerala’s Response
In response to the recent suspected Nipah virus cases in Kozhikode district, the Kerala government has initiated a comprehensive strategy. A high-level meeting led by Kerala’s Health Minister, Veena George, has been convened to assess the situation and coordinate efforts. The government has taken several measures, including contact tracing, isolating the affected individuals, and quarantining those who may have been exposed to the virus.
The Role of Public Awareness
Public awareness campaigns are pivotal in controlling the spread of the Nipah virus. It is essential for individuals to understand the modes of transmission, recognize early symptoms, and seek medical attention promptly if they suspect infection. Simple preventive measures, such as avoiding close contact with bats and refraining from consuming fruits with visible bat-related damage, can reduce the risk of transmission.
Conclusion
The reappearance of the Nipah virus in Kerala serves as a stark reminder of the ongoing challenges in combating infectious diseases. While Kerala had effectively managed previous outbreaks, the resurgence of the virus underscores the need for constant vigilance and robust public health measures. The state government’s swift response and public awareness efforts are critical in containing the spread of this deadly virus. As Kerala confronts this renewed health threat, the world watches, hoping that the lessons learned from previous encounters with Nipah will aid in its containment once more.
Buy Immunity Booster : Click Here
more: AIIMS: Pioneering Healthcare and Medical Research in India
























[…] […]